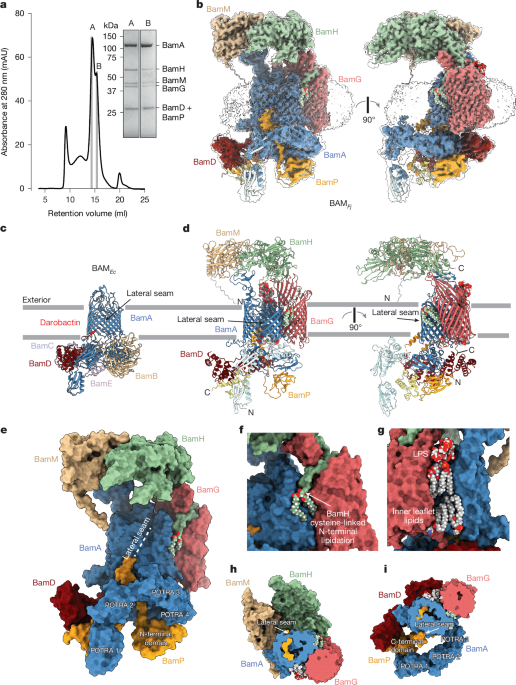
"The BamA barrel has a periplasmic extension composed of five polypeptide transport-associated (POTRA) domains to which the lipoprotein subunits bind7,8,9. Within the BamA barrel the seam between the first and last strands is unusually short and can open7,9, exposing the N-terminal strand of the BamA barrel to pair with the C-terminal strand of an incoming substrate OMP10,11. This structure in turn acts as a template for insertion and folding of successive strands of the nascent OMP through β-augmentation."
"The Bacteroidota are a phylum of abundant Gram-negative commensals found in the human gut and other human microbiomes12 that includes major opportunistic anaerobic pathogens that are responsible for sepsis (for example, Prevotella species and Bacteroides fragilis) and severe dental disease ( Porphyromonas gingivalis). OM proteins in the Bacteroidota exhibit considerably greater structural diversity than the OM proteome of E. coli, raising the possibility that the Bacteroidota BAM machinery might be functionally augmented relative to BAMEc."
E. coli BAM comprises the outer membrane protein BamA plus four periplasmic lipoprotein subunits, with only BamA and BamD individually essential for function. BamA forms a 16-stranded β-barrel with five POTRA domains that bind lipoproteins. The short seam between the first and last BamA strands can open, allowing the BamA N-terminal strand to pair with a substrate OMP C-terminal strand and template insertion and folding of successive nascent strands via β-augmentation. This process forms a transient hybrid barrel that resolves when the substrate completes folding and releases. Bacteroidota species have greater OM protein structural diversity, larger extracellular OMP domains, and abundant cell surface lipoproteins, implying a need for an augmented BAM capacity to assemble these substrates.
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]