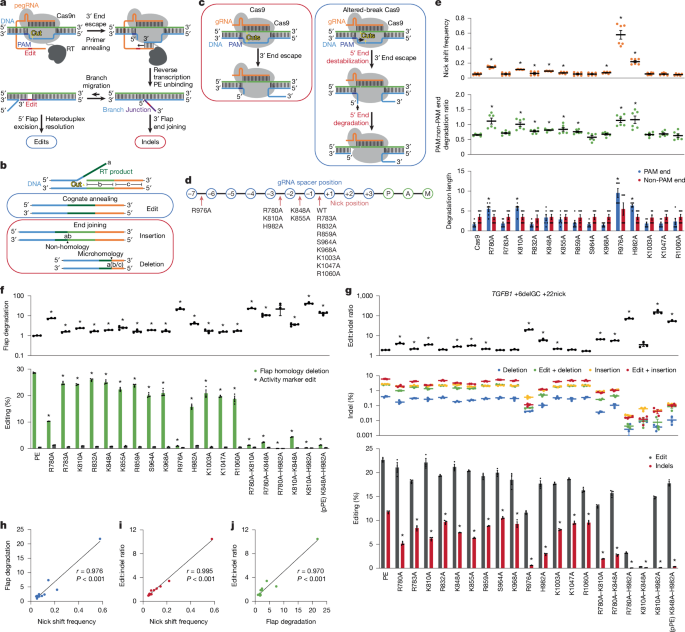
"Prime editors are advanced CRISPR tools that enable replacement of targeted DNA with programmed sequences3. A prime editor comprises a Cas9 nickase (Cas9n) fused to a reverse transcriptase and paired with an extended guide RNA (pegRNA) that encodes both the genomic target sequence and the intended edit1. Editing initiates with the prime editor binding its genomic target and forming a single-strand DNA break (nick; Fig. 1a)."
"A key remaining challenge is the elimination of errors that occur as byproducts of prime editing. These errors are insertion and deletion (indel) mutations generated in lieu of the intended edit within a fraction of targeted cells, resulting in DNA sequences that are unpredictable and possibly deleterious2,17. Previous work has identified major drivers of indel error formation, although the mechanisms have not been fully elucidated."
Prime editors combine a Cas9 nickase fused to a reverse transcriptase with an extended guide RNA (pegRNA) to replace targeted DNA with programmed sequences. Editing starts with nick formation, release of the 3′ DNA end, annealing to the pegRNA template, and reverse transcription to extend the 3′ end, which can displace the 5′ strand to install edits. Prime editing supports substitutions, insertions, and deletions. Efficiency improvements include mismatch repair inhibition, pegRNA stabilization, and reverse transcriptase engineering. A prominent remaining issue is indel byproducts arising from events such as pegRNA scaffold extension and errant double-strand breaks, sometimes linked to mismatch repair.
Read at Nature
Unable to calculate read time
Collection
[
|
...
]